Protein Crosslinkers for Biological Applications
Time:2023-09-27 Hits:407
|
Crosslinking refers to the process of chemically joining two or more molecules together through covalent bonds. Crosslinkers contain reactive ends that can react under mild conditions with specific functional groups (such as primary amines and thiols) located on proteins or other biomolecules (DNA, RNA, lipids, and sugars). Thus, crosslinkers are often used to modify nucleic acids, drugs, and solid phase carrier surfaces in a process called bioconjugation, which includes crosslinking, immobilization, surface modification, and biomolecular labeling.
|
1.The main classification of protein crosslinkers (terminal active groups ):
Protein crosslinkers generally need to meet PH sensitivity, specific enzyme sensitivity, cleavage, non-cleavage and other conditions, commonly used ligation bonds such as hydrazone bonds, disulfide bonds, peptide bonds, glucose bonds, thioether bonds and maleimide bonds and so on. Therefore, protein crosslinkers are mainly concentrated into the following categories according to their structure and application:
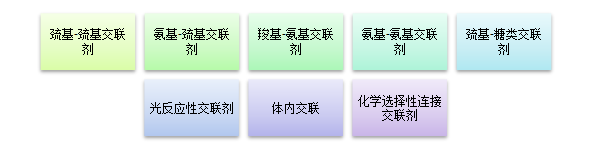
(1)SH-SH crosslinker
(2)NH2-SH crosslinker
(3)COOH-NH2 crosslinker
(4)NH2-NH2 crosslinker
5)SH-Saccharides crosslinker
(6)Photoreactive crosslinker
(7)Chemically selective linkage crosslinkers
To maintain the enzymatic bioactivity of enzymes and the immunobinding activity of antibodies during enzyme-antibody coupling, in addition to improving crosslinking methods, the development of various new structural and functional crosslinking agents is of great importance. For instance, short-chain heterobifunctional crosslinkers like Succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate (SPDP) can form degradable disulfide bonds by reacting with cysteine thiol groups through NHS-esters and pyridyl dithiol reactive moieties. The combination of amine and thiol groups enables controlled crosslinking, enhancing selectivity and product uniformity.
Therefore, protein crosslinking agents with two different reactive groups have garnered more attention due to their ability to facilitate controlled crosslinking reactions.
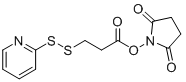 CAS# 68181-17-9 SPDP 2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl?3-(pyridin-2-yldisulfaneyl)propanoate |
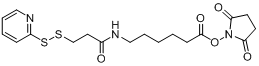 CAS#158913-22-5 LC-SPDP 2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl?6-(3-(pyridin-2-yldisulfaneyl)propanamido)hexanoate |
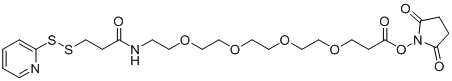 CAS# 1334177-95-5 SPDP-PEG4-NHS ester |
|
2.Key Applications of Protein Crosslinking Agents:
Protein-Protein Interactions
Most protein-protein interactions are transient, and crosslinking methods can be employed to stabilize or permanently link components within interaction complexes, aiding in the identification of these momentary contacts. The study of protein-protein interactions is crucial for a better understanding of biological phenomena and holds significant biological relevance. The rapidly advancing Chemical Cross-Linking Mass Spectrometry (CL-MS) technique, achieved through the optimization of various crosslinkers, is used to analyze protein structures and protein-protein interactions.
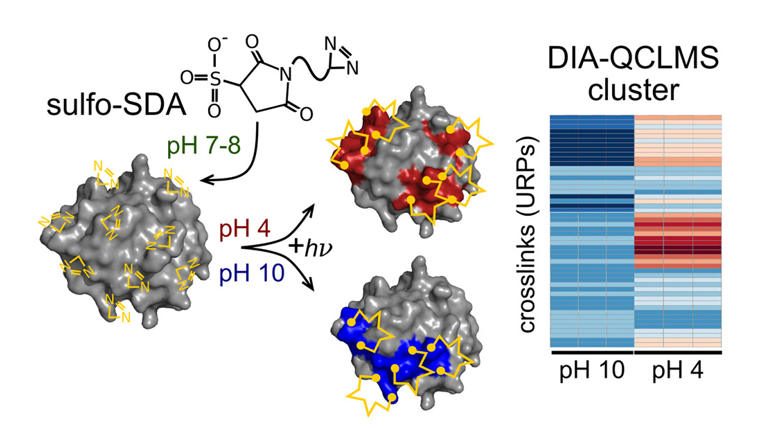 `
`Photo-crosslinking well coupled with QCLMS[2]
Ligation of carrier proteins to haptens
A peptide sequence (hapten) of a virus-coated protein can be linked to a carrier protein to make a vaccine to stimulate an immune response. In addition, monoclonal antibodies are prepared and used to return to find antigen-binding sites on macromolecular proteins. The crosslinker is adjusted to result in a lower molar ratio of hapten-carrier proteins with higher antibody affinity.
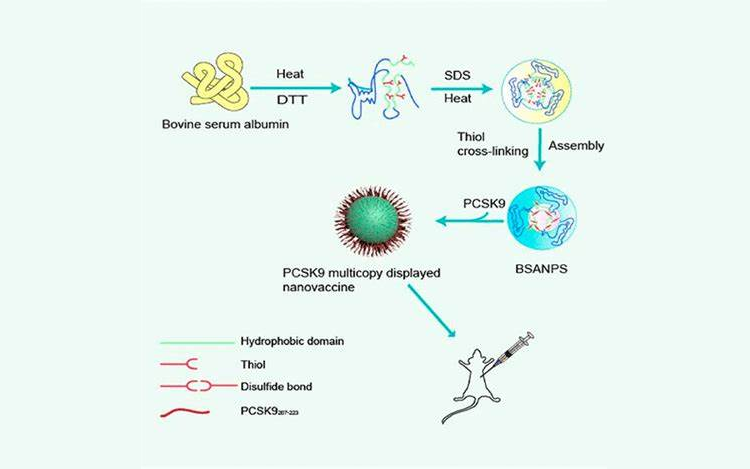 `
`PCSK9 Multicopy Displayed Nanovaccine[3]
Solidification of proteins or other molecules
The protein pass is covalently bound to various crosslinkers with different properties on solid matrices such as magnetic beads, 96-well plates, glass, etc., to adapt to different target analysis or substances that need to be adsorbed or for storage, etc., while reducing losses during elution processes.
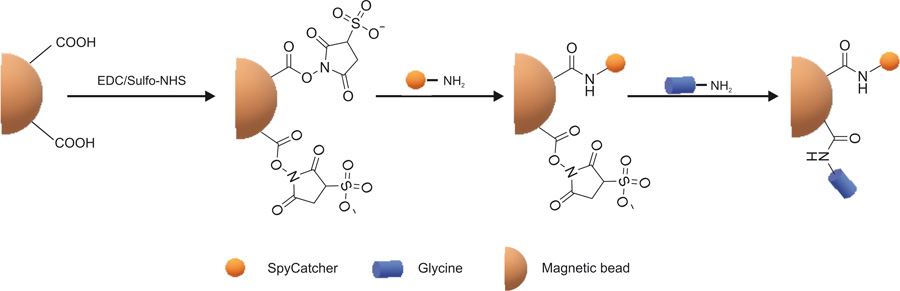 `
`The preparation of SC-coupled magnetic beads[4]
Labeling of antibodies, marker transfer
Antibodies are linked to enzymes, fluorophores or biotin for quantitative measurements or positional observations. Biotin-containing crosslinker substances and labeled streptavidins are widely used in bioanalytical and bioassays such as flow cytometry, ELISA, immunohistochemical staining, western blotting, etc.。
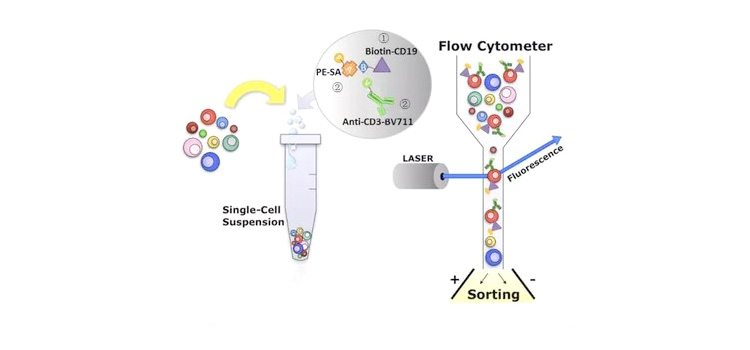 `
`Diagrammatic drawing OF Flow cytometry from Bioon
|
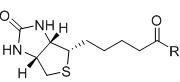
 CAS# 58-85-5 Vitamin H |
 CAS#66640-86-6 Biotin Hydrazied |
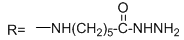 CAS# 109276-34-8 Biotin-LC-Hydrazide |
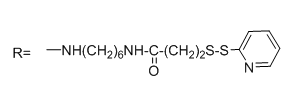 CAS# 129179-83-5 N-[6-(Biotinamido)hexyl]-3'-(2-pyridyldithio)propionamide |
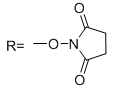 CAS# 35013-72-0 N-(D-Biotinyloxy)succinimide |
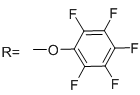 CAS# 120550-35-8 Biotin-PFP |
|
Research on Targeted Drugs
Antibodies that recognize tumor surface antigens and drugs are covalently linked through cross-linking agents to achieve targeted therapy, thereby reducing the killing of healthy cells by traditional chemotherapy methods. Drug-linker-carrier conjugate, well improve and control the transport and metabolism of drugs in the body, realize sustained release administration and directed administration, improve bioavailability and therapeutic index, and meet the requirements of vector drugs that need to be quantified and released in vivo.
In recent years, through the selection of specific cross-linkers and the clever use of the interaction between cross-linkers and proteins, new therapeutic methods such as ADC and PROTAC, which are mainly used to study cancer treatment, have achieved rapid results.
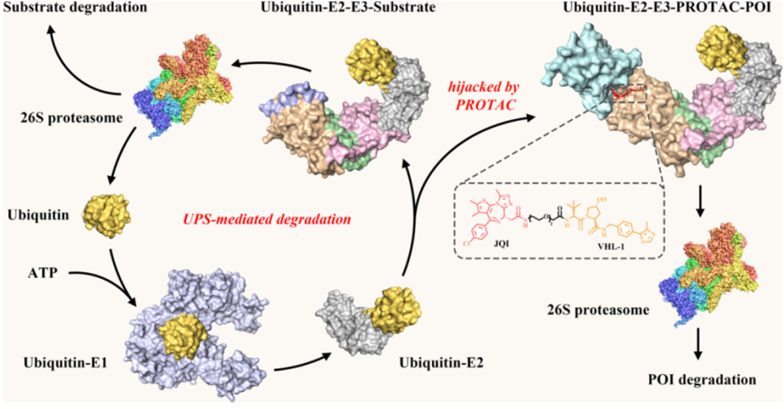 `
`Mechanism of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs)[5, 6]
3.Targeted Drug Selection for Protein Crosslinking Agents Requires Meeting Two Criteria:
(1) Maintaining drug stability in the bloodstream.
(2) Ensuring effective drug release within target cells once it reaches tumor tissue.
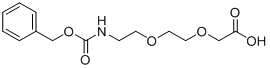 CAS# 165454-06-8 3-Oxo-1-phenyl-2,7,10-trioxa-4-azadodecan-12-oic acid |
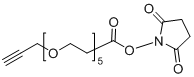 CAS# 1393330-40-9 Propargyl-PEG5-NHS Ester> |
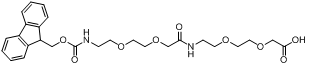 CAS# 560088-89-3 Fmoc-AEEA-AEEA |
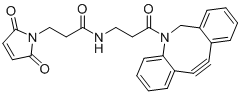 CAS# 1395786-30-7 DBCO-Maleimide |
References
- Laurent, D.; Bernhard, S. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 5–13
- G.M. Dubowchik;R. A.Frestone. Bioconjugate Chem. 2002,13,855.
- Y.Yoneda, S.C.J.Steinige. Bioorg Med Chen.Lett 2008,18,1632.
- M. Dorywalika, P Strop et al, Bioconjiagote Chem.2015,26,650.
- Komander D, Rape M. The ubiquitin code. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:203–29.
- Yau R, Rape M. The increasing complexity of the ubiquitin code. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18(6):579–86.
4.Protein Crosslinking Agent Product Series
Seebio Biotech is pleased to introduce an expanded range of protein crosslinking agent products. Users can conveniently explore further details on our official website.

|
Target group-1
|
Target group2
|
Linkers
|
||
|
NH2-
|
COOH
|
Carboxyl Group-(Spacer)-Amino Group
|
56-40-6
|
AAU0115A,Glycine,100G 1KG 5KG
|
| 107-95-9 | AAU0116A, β-Alanine,100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 56-12-2 | AAU0117A, 4-Aminobutyric acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 660-88-8 | AAU0118A, 5-Aminopentanoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 60-32-2 | AAU0119A, 6-Aminocaproic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 929-17-9 | AAU0120A, 7-Aminoheptanoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 693-57-2 | AAU0121A, 12-Aminododecanoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| NHS Ester-Boc Amino | 51513-80-5 | AAU0009A, 6-(N-Boc)caproic acid NHS, 5G 25G 100G | ||
|
SH-
|
NHS Ester-Maleimide | 55750-62-4 | AAU0122A, N-Succinimidyl 3-maleimidopropionate(BMPS), 25G 100G | |
| 80307-12-6 | AAU0123A, 4-Maleimidobutyric acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester(GMBS), 25G 100G | |||
| 55750-63-5 | AAU0124A, 6-Maleimidocaproic acid-NHS (EMCS), 25G 100G | |||
| 87981-04-2 | AAU0038A, Maleimide-C10-NHS ester, 25G 100G | |||
| 64987-85-5 | AAU0125A, N-SucciniMidyl 4-(N-MaleiMidoMethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylate(SMCC), 25G 100G | |||
| 92921-24-9 | AAU0126A, 4-(N-Maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid 3-sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester sodium salt(Sulfo-SMCC), 25G 100G | |||
| 58626-38-3 | AAU0127A, 3-Maleimidobenzoic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester, 1G 5G | |||
| 79886-55-8 | AAU0060A,4-(4-Maleimidophenyl)butyric acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester(SMPB), 1G 5G | |||
| 125559-00-4 | AAU0177A, N-SucciniMidyl 6-[[4-(N-MaleiMidoMethyl)cyclohexyl]carboxaMido]hexanoate(LC-SMCC), 500MG 1G | |||
| Carboxyl -Maleimide | 7423-55-4 | AAU0130A, 3-Maleimidopropionic acid(MPA), 100G 1KG 5KG | ||
| 57078-98-5 | AAU0019A, 4-Maleimidobutyric acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 55750-53-3 | AAU0131A, 6-Maleimidocaproic acid(EMCA), 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 25021-08-3 | AAU0023A, 2-Maleimido acetic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 68181-17-9 | AAU0113A, 3-(2-Pyridyldithio)propionic acid N-succinimidyl ester,5G 25G | |||
| Carboxyl -Disulfide | 1077-28-7 | AAU0001A, DL-α-Lipoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | ||
|
-C≡C-/Cyclooctyne
|
Carboxyl -Alkyne/Cyclooctyne | 53293-00-8 | AAU0065A, 5-Hexynoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |
| 2777-65-3 | AAU0044A, 10-Undecynoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 6089-09-4 | AAU0031A, 4-Pentynoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
|
-C≡C-/Cyclooctyne
|
Carboxyl--Azide | 79583-98-5 | AAU0003A, 5-Azidopentanoic acid, 100G 1KG 5KG | |
| Other | NHS Ester--Acrylic | 38862-24-7 | AAU0034A, N-Acryloxysuccinimide, 100G 1KG 5KG | |
| 38862-25-8 | AAU0033A, N-Succinimidyl methacrylate, 25G 100G | |||
| NHS Ester-Other | 42014-51-7 | AAU0138A, Bromoacetic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester, 1G 5G 25G | ||
| 39028-27-8 | AAU0091A, Iodoacetic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester, 1G 5G | |||
| 60444-78-2 | AAU0039A, 4-甲酰苯甲酸 N-琥珀酰亚胺酯,25G 100G | |||
| -COOH | SH- | Amino -Maleimide | 134272-64-3 | AAU0097A, N-(2-Aminoethyl)maleimid trifluoroacetate salt, 5G 25G |
| Amino-Thiol | 60-23-1 | AAU0068A, 2-Aminoethanethiol, 100G 1KG 5KG | ||
| N3- | Amino -Alkyne/Cyclooctyne | 1255942-06-3 | AAU0139A, Dibenzocyclooctyne-amine(DBCO-Amine), 5G 25G | |
| 2450-71-7 | AAU0056A, Propargylamine,100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| -C≡C-/Cyclooctyne | Amino -(Spacer)-Azide | 88192-19-2 | AAU0071A, 3-Azido-1-propanamine, 5G 25G | |
| CHO- | SH- | Hydrazide -Maleimide | 151038-94-7 | AAU0142A, 6-(2,5-Dioxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)hexanehydrazide 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate, 5G 25G |
| N3- | Maleimide Group-Alkyne/Cyclooctyne | 1395786-30-7 | AAU0013A, Dibenzocyclooctyne-maleimide(DBCO-maleimide), 1G 5G | |
| 209395-32-4 | AAU0028A, N-Propargylmaleimide, 5G 25G | |||
| N3 | Other | Alkyne-Hydroxy | 927-74-2 | AAU0144A, 3-Butyn-1-ol, 100G 1KG 5KG |
| 928-90-5 | AAU0145A, 5-Hexyn-1-ol, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 63478-76-2 | AAU0146A, 6-Heptyn-1-ol,100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 5390-04-5 | AAU0147A, 4-Pentyn-1-ol, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 871-91-0 | AAU0148A, 7-Octyn-1-ol, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 17643-36-6 | AAU0149A, 9-Decyn-1-ol, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| 2774-84-7 | AAU0150A, 10-Undecyn-1-ol, 100G 1KG 5KG | |||
| Cyclooctyne-Hydroxy | 1263166-90-0 | AAU0151A,(1R,8S,9s)-Bicyclo[6.1.0]non-4-yn-9-ylmethanol(BCN-OH),1G 5G | ||
5.Featured Product Recommendations
Copper-Free Crosslinking
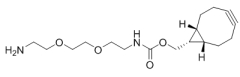 AAU0103A; 1G 5G CAS# 1263166-93-3 CN-POE3-NH2 |
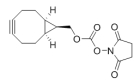 AAU0105A; 1G 5G CAS# 1426827-79-3 BCN-CO-NHS |
Light crosslinking
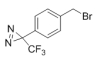 AAU0095A; 5G 25G CAS# 92367-11-8 4-[3-(Trifluoromethyl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl]benzyl Bromide |
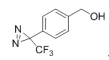 AAU0062A; 5G 25G CAS# 87736-88-7 4-[3-(Trifluoromethyl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl]benzyl Alcohol |
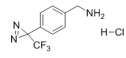 AAU0041A; 5G 25G CAS# 1258874-29-1 4-[3-(Trifluoromethyl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl]benzylamine Hydrochloride |
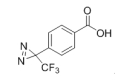 AAU0040A; 5G 25G CAS# 85559-46-2 4-[3-(Trifluoromethyl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl]benzoic Acid |
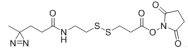 AAU0109A; 1G 5G; CAS# 1253202-38-8 NHS-SS-Diazirine (SDAD) |
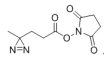 AAU0108A; 1G 5G CAS# 1239017-80-1 NHS-Diazirine (SDA) |
|
|
Associated reagents
|
AAU0152A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 156-57-0 Cysteamine Hydrochloride |
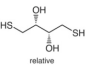 AAU0153A; 100g 1KG 5KG CAS# 3483-12-3 Cleland's Reagent |
AAU0166A, 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 3945-69-5 DMTMM |
AAU0155A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 56-17-7 Cystamine Dihydrochloride |
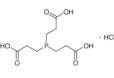 AAU0156A; 100g 1KG 5KG CAS# 51805-45-9 Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine Hydrochloride |
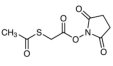
AAU0133A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 76931-93-6 N-Succinimidyl S-Acetylthioglycolate |
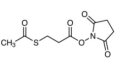 AAU0092A; 100g 1KG 5KG CAS# 84271-78-3 N-Succinimidyl 3-(Acetylthio)propionate |
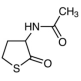
AAU0157A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 1195-16-0 3-Acetamidotetrahydro-2-thiophenone |
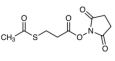
AAU0158A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 69-78-3 5,5'-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic Acid) |
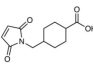
AAU0159A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 64987-82-2 4-(N-Maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid |
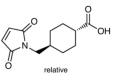 AAU0160A; 100g 1KG 5KG CAS# 69907-67-1 trans-4-(N-Maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic Acid |
AAU0161A; 100g 1KG 5KG
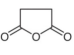
CAS# 108-30-5 Succinic Anhydride |
AAU0173A; 100g 1KG 5KG
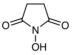
CAS# 6066-82-6 N-Hydroxysuccinimide |
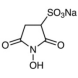 AAU0174A; 100g 1KG 5KG CAS# 106627-54-7 N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide Sodium Salt |
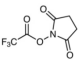
AAU0175A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 5672-89-9 N-Succinimidyl Trifluoroacetate |
AAU0176A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 25895-60-7 Sodium Cyanoborohydride |
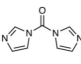
AAU0162A 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 530-62-1 1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole |
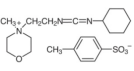
AAU0163A; 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 2491-17-0 CMC |
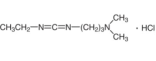
AAU0164A 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS#25952-53-8 EDCI·HCl |
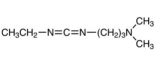
AAU0165A 100g 1KG 5KG
CAS# 1892-57-5 EDC |
Related Products
